Decarbonization
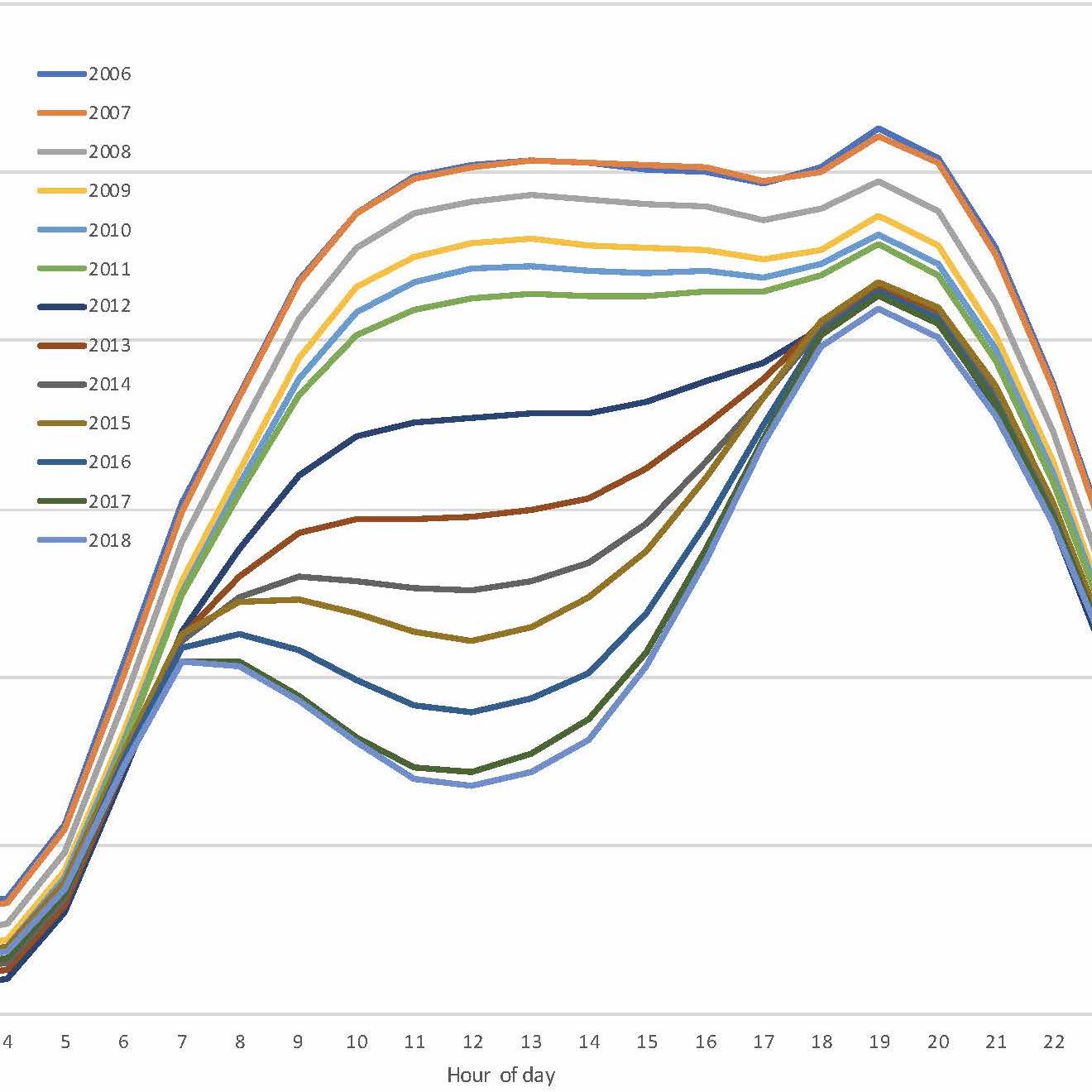
This project integrates data science and machine learning into engineering and economics frameworks to address challenges in creating smart grid power systems of the future. In particular, this takes into account the unique mix of power sources (involving substantial amount of rooftop solar due to its geography), combined with its isolated grid.
Research includes dynamic electricity pricing based on supply and demand; reinforcement learning to control home appliances; federated learning at the grid edge for enhanced security and privacy; and policies to implement transition to smart grids and assistance to low-income households to enable the economics of the transition, where machine learning is instrumental.
Hawaii has high penetration of renewable energy and an exceptionally high share of households with rooftop solar systems in the United States. Thus Hawaii and the UHM campus form a natural `living laboratory’ to conduct experiments to evaluate and validate the research that can also be used to integrate technologies such as smart homes, ability to schedule usage, and integrating increasing amounts of power generation from consumers. The combination of engineering with business and economics helps with transitioning to grid monetizations based on quality of service and other metrics that can avoid the utility death spiral in the business model.
Decarbonization pathways
Descartes applies data science to address critical needs in the pathway to decarbonization.
Efficiency of renewables integration
Descartes investigates the socioecomic impacts of renewables integration.